BONE and JOINT INFECTIONS
Introduction
OSTEOMYELITIS
เป็นภาวะการอักเสบของเนื้อเยื่อกระดูกหรือไขกระดูก ส่วนใหญ่เกิดจากการติดเชื้อ อาจเป็นแบบฉับพลันหรือเรื้อรัง ส่งผลให้มีการทำลายของกระดูก เกิดเซลล์กระดูกตาย (bone sequestration) หรือ sinus formations/fistula) หรือ sepsis ซึ่งมีอันตรายถึงชีวิต การรักษาอย่างรวดเร็วและเหมาะสมช่วยยับยั้งการแพร่กระจายของเชื้อ และป้องกันการเกิด complication ที่รุนแรงได้
CLINICAL
Pathogenesis
ส่วนใหญ่เกิดจากเชื้อที่แพร่ผ่านจากกระแสเลือด (hematogenous osteomyelitis) รองลงมาเป็นการแพร่เชื้อจากเนื้อเยื่อใกล้เคียงที่ติดเชื้อ หรือ penetrating trauma หรือ iatrogenic causes เช่น joint replacements, internal fixation of fractures, secondary periapical periodontitis เป็นต้น ผู้ป่วยที่มีระบบภูมิคุ้มกันบกพร่อง หรือได้รับยากดภูมิคุ้มกัน รวมทั้งผู้ป่วยเบาหวาน มีโอกาสเกิดการติดเชื้อได้ง่ายขึ้น
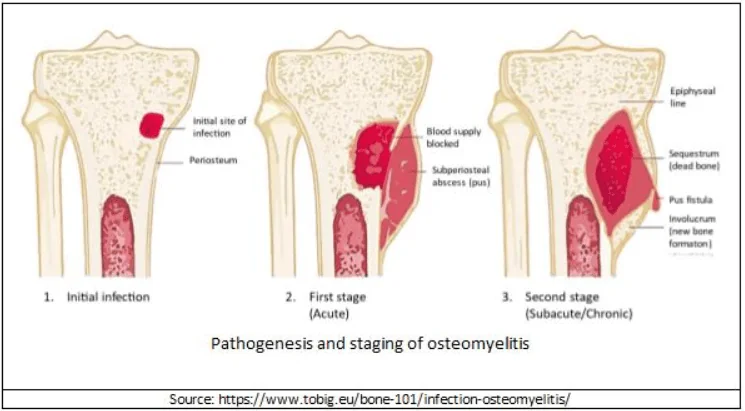
ภาวะการอักเสบแบ่งตามระยะการดำเนินโรคหากไม่ได้รับการรักษาประกอบด้วย
- Acute osteomyelitis คือ การอักเสบเกิดขึ้นในเวลา 2 สัปดาห์ ในตำแหน่งที่ไม่เคยมีการติดเชื้อมาก่อน จะพบมี neutrophil จำนวนมาก และตรวจพบเชื้อก่อโรคได้บ่อย
- Subacute หรือ chronic osteomyelitis เกิดในระยะเวลาเป็นเดือนหรือหลายเดือน ซึ่งจะพบ necrotic bone (involucrum), fibrosis, granulation และ mononuclear cell แต่พบเชื้อก่อโรคได้น้อย ระยะนี้ ก่อให้เกิด bone sclerosis และ deformity ของโครงกระดูก
Diagnosis
ในผู้ใหญ่อาการมักไม่ชัดเจน ส่วนใหญ่มาด้วยอาการกึ่งเฉียบพลันหรือเรื้อรัง มีอาการปวดบริเวณที่มีการติดเชื้อแต่มักไม่มีอาการไข้หรืออาการตามระบบ ส่วนน้อยอาจพบการอักเสบเฉพาะที่เหนือต่อตำแหน่งที่ติดเชื้อ ในรายที่เป็นมานานหลายเดือนหรือเป็นปี อาจพบ draining sinus tract จากตำแหน่งที่ติดเชื้อร่วมด้วย การวินิจฉัยที่สำคัญ คือต้องคิดถึงโรคนี้ในผู้ที่มีปัจจัยเสี่ยง ร่วมกับมีอาการเฉพาะที่
การส่งตรวจเพิ่มเติม
- CBC, ESR, CRP
- Culture
⇒ ส่งเพาะเชื้อจากสิ่งส่งตรวจที่เจาะดูดจากกระดูกภายใน แต่บางครั้งทำได้ยาก การเพาะเชื้อจากแผลหรือหนองต้องแปลด้วยความระมัดระวังเนื่องจากอาจเป็นเชื้อที่ colonization บนผิวหนัง
⇒ ผลการเพาะเชื้อจากเลือดใน hematogenous osteomyelitis ให้ผลบวกเพียง 50% - การตรวจทางรังสีวิทยา:
⇒ ใน acute osteomyelitis อาจพบเพียง adjacent soft tissue swelling
⇒ หลังการติดเชื้อประมาณ 14-21 วัน การเปลี่ยนแปลงของกระดูกจะพบการยกตัวของเยื่อหุ้มกระดูก (periosteal elevation)
⇒ หลังการติดเชื้อประมาณ 2-6 สัปดาห์ จะพบ lytic changes - อาจพิจารณาส่งตรวจ CT scan, MRI หรือ Radionuclide bone scanning ตามความเหมาะสม
COMMON PATHOGENS
เชื้อก่อโรคที่พบบ่อยคือ S. aureus ทั้งนี้ การติดเชื้ออาจเกิดจากเชื้อชนิดอื่นขึ้นกับโรคประจำตัวหรือปัจจัยที่เกี่ยวข้อง
ปัจจัยเสี่ยงและชนิดของเชื้อก่อโรค osteomyelitis ที่พบบ่อย
| ปัจจัยที่เกี่ยวข้อง | เชื้อก่อโรคที่พบบ่อย |
| Osteomyelitis ทุกชนิด | S. aureus |
| Children | S. aureus, streptococci, H. influenzae, enteric Gram-negative bacilli |
| Prosthesis or instrument implantation | S. aureus, coagulase-negative staphylococci, Cutibacterium acnes, Propionebacterium spp. |
| Nosocomial infections | Enterobacteriaceae, P. aeruginosa |
| Contaminated open fracture | S. aureus, streptococci, enterococci, enteric Gram-negative bacilli หรือ mixed organisms |
| Bite injury | Oral streptococci, anaerobes, P. multocida (cat bite), E. corrodens (human bite) |
| Diabetic foot infection, decubitus ulcer | S. aureus, streptococci, enterococci, enteric Gram-negative bacilli, P. aeruginosa หรือ mixed organisms |
| Hemoglobinopathies | Salmonella spp., S, pneumoniae |
| AIDS | Bartonella henselae, mycobacteria, C. neoformans, dimorphic fungi |
| Immunocompromised patients | Mycobacteria, fungi |
| Living in an endemic area | M. tuberculosis, Brucella spp., Coxiella burnetii, dimorphic fungi of specific pathogens |
TREATMENTS
General Principle
หลักการรักษาที่สำคัญคือการให้ยาต้านจุลชีพ ร่วมกับการผ่าตัด debridement เพื่อกำจัดการติดเชื้อและเนื้อตาย และการฟื้นฟูสภาพหลังรักษา ทั้งนี้ การเลือกยาต้านจุลชีพ ขึ้นกับชนิดของการอักเสบของกระดูก ในราย Acute osteomyelitis ที่เกิดจาก hematogenous osteomyelitis ที่มีอาการตามระบบ หรือเกิดภาวะแทรกซ้อนที่สำคัญ เช่น sepsis syndrome, spinal cord compression ควรให้ยาต้านจุลชีพ empiric systemic antibiotic ที่ครอบคลุมเชื้อโรคที่เป็นไปได้ ส่วนในรายที่เกิดจาก contiguous focus of infection หรือ chronic osteomyelitis ที่ไม่มีอาการตามระบบ ควรเก็บสิ่งส่งตรวจก่อนให้ยาต้านจุลชีพ และเลือกใช้ยาต้านจุลชีพที่มีระดับยาในกระดูกสูงมีฤทธิ์แบบ bactericidal หลังทราบผลการเพาะเชื้อพิจารณาปรับเปลี่ยนยาตามความเหมาะสม
Definitive Antimicrobial Treatment
| เชื้อก่อโรค | ยาปฏิชีวนะ first choice | Alternative choice |
| Staphylococcus spp. – Oxacillin sensitive |
• Cloxacillin 2 g q 4-6 hours for 4-6 weeks or • Cefazolin 1-2 g IV q 8h for 4-6 weeks |
• Vancomycin 15 mg/kg IV q 12h for 4-6 weeks; • Some add Rifampin 600 mg PO OD to cloxacillin |
| Oxacillin resistant (MRSA) | • Vancomycin 15 mg/kg IV q 12h for 4-6 weeks | • Linezolid 600 mg PO/IV for 6 weeks or • Levofloxacin 500-750 mg PO/IV daily + Rifampin 600-900 mg/day PO for 6 weeks if susceptible to both drugs |
| Streptococcus spp. Penicillin sensitive |
• Penicillin G 20 MU/in 24 hours equally divided daily for 4-6 weeks or • Ceftriaxone 2 g iv or im q 24 hours for 4-6 weeks or • Cefazolin 1-2 g iv q 8 hours for 4-6 weeks |
• Vancomycin 15 mg/kg IV q 12 hours for 4-6 weeks |
| Enterococcus spp. or Streptococcus spp. with MIC ≥ 0.5 ug/ml, or Abiotrophia or Granulicatella spp. | • Penicillin G 20 MU/in 24 hours equally divided daily for 4-6 weeks or • Ampicillin 12 g/ 24 hours in 6 equally divided daily doses: the addition of gentamicin 1 mg/kg IV or IM q 8h for 1-2 weeks is optional |
• Vancomycin 15 mg/kg IV q 12h for 4-6 weeks: the addition of gentamicin 1mg/kg IV or im q 8h for 1-2 weeks is optional |
| Enterobacteriaceae | • Ceftriaxone 1-2 g IV q 24 hours for 4-6 weeks or • Ertapenem 1 g IV q 24 hours |
• Ciprofloxacin 500-750 mg PO q 12h for 4-6 weeks or • Levofloxacin 500-750 mg PO q 24 hours |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
• Cefepime 2 g IV q 8-12 hours or • Meropenem 1 g IV q 8h or • Imipenem 500 mg IV q 6 hours for 4-6 weeks |
• Ciprofloxacin 750 mg PO q 12h for 4-6 weeks or • Ceftazidime 2 g IV q 8h |
OTHER RESOURCES
OTHER RESOURCES
References
1. อนุภพ จิตต์เมือง. Bone and Joint Infections. Handbook of Infectious Disease [Book Editors: รุจิภาส สิริจตุภัทร, ภาคภูมิ พุ่มพวง, วลัยพร วังจินดา]. 2nd. กรุงเทพมหานคร : สาขาวิชาโรคติดเชื้อและอายุรศาสตร์เขตร้อน ภาควิชาอายุรศาสตร์ คณะแพทยศาสตร์ ศิริราชพยาบาล มหาวิทยาลัยมหิดล, 2021, pp. 201-208.
2. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s. Osteomyelitis. Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. ninth. s.l. : Elsevier, Inc., 2020, p. 104.
3. Sara Keller, M.D. Osteomyelitis (Acute and Chronic). Johns Hopkins ABX Guide. The Unbound platform 2000-2022. s.l. : Johns Hopkins University, 2020.
