BONE and JOINT INFECTIONS
Introduction
INFECTIOUS ARTHRITIS
ข้ออักเสบจากการติดเชื้อภายในข้อและเนื้อเยื่อที่เป็นส่วนประกอบของข้อ ส่งผลให้พยาธิสภาพของ joint fluid เปลี่ยนไปในลักษณะทำลายมากกว่าจะเป็นตัวหล่อลื่น หากไม่ได้รับการรักษาทันท่วงทีแล้ว destructive joint จะเกิด fibrous หรือ bony ankylosing และ deformity ตามมา การติดเชื้อลุกลามเกิดเป็น chronic sinus drainage หรือ septicemia ทำให้ผู้ป่วยเสียชีวิตในที่สุดได้
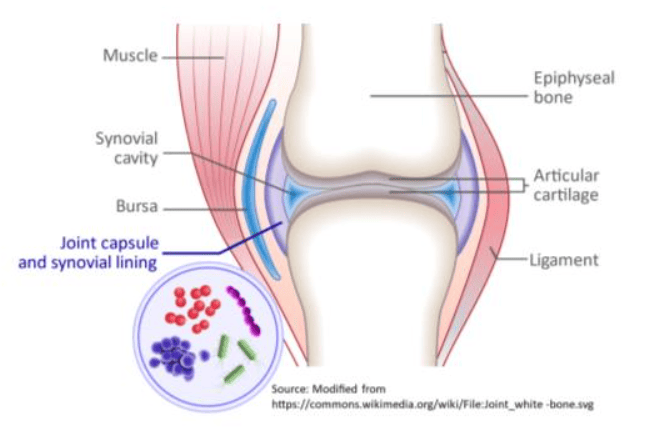
CLINICAL
ส่วนใหญ่เป็นเพียงข้อเดียว (monoarticular involvement) แต่อาจพบหลายข้อได้ ในผู้ใหญ่ที่พบบ่อยคือ knee รองมาได้แก่ hip และ ankle joint ในขณะที่ neonate มักจะเป็นมากที่ hip joint ลักษณะทางคลินิกแบ่งเป็น acute infectious arthritis และ subacute หรือ chronic infectious arthritis
COMMON PATHOGENS
เชื้อก่อโรคที่พบบ่อยตามลักษณะทางคลินิก
- Acute infectious arthritis: กลุ่มแบคทีเรีย จำแนกเป็น 2 กลุ่ม ได้แก่ gonococcal arthritis หรือ disseminated gonococcal infection จากเชื้อ N. gonorrhoeae และ non-gonococcal bacterial arthritis แบคทีเรียอื่นๆ
- Subacute หรือ Chronic infectious arthritis: เชื้อกลุ่ม mycobacterium หรือเชื้อรา
เชื้อก่อโรคที่พบบ่อยตามปัจจัยเสี่ยงที่เกี่ยวข้อง
| เชื้อก่อโรค | ปัจจัยที่เกี่ยวข้อง |
| Staphylococcus aureus | Rheumatoid arthritis, IVDU, post-arthroscopy/arthrotomy, infective endocarditis, prior หรือ concurrent periarticular skin/soft tissue infection |
| Coagulase-negative staphylococci | Post-arthroscopy/arthrotomy, prosthesis implantation |
| Streptococci | Elderly, chronic medical illness, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, liver disease, malignancy, immunocompromised host, on immunosuppressive agent |
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae | Sexually active young person, previous sexually transmitted disease, unsafe sex, menstruation, pregnancy |
| Enteric Gram-negative bacteria | Elderly, chronic medical illness, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, liver disease, malignancy, immunocompromised host, on immunosuppressive agent |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | IVDU |
| Burkholderia pseudomallei | Diabetes, chronic kidney disease, liver disease, alcoholism, occupational exposure |
| Oral microbiota, anaerobes, Pasteurella multocida, Capnocytophaga spp., Eikenella corrodens |
Dog or cat bite, human bite (E. corrodens) |
| Kingella kingae | Children, younger age |
| Viruses | Children, younger age |
| Mycobacterium tuberculosis | Prior หรือ recent tuberculosis, chronic medical illness, immunocompromised host, on immunosuppressive agent |
| Non-tuberculous mycobacteria | immunocompromised host, on immunosuppressive agent, exposure to aquatic environment (M. marinum) |
| Candida spp., Aspergillus spp. |
Prior หรือ recent invasive infection, neutropenia |
| Sporothrix schenckii | ประวัติ trauma ที่มี exposure ต่อ colonized soil หรือ plants |
การวินิจฉัยเบื้องต้นเพื่อจำแนกชนิดของเชื้อก่อโรคจากผลตรวจ synovial fluid
| Normal synovial fluid | Non-infectious inflammatory arthritis* | Acute bacterial arthritis | Mycobacterial หรือ fungal arthritis |
|
| จำนวนWBC count (cell/µl) | <180 | < 30,000 – 50,000 | 25,000 – 250,000 | 10,000 – 30,000 |
| ชนิดของ WBC | Mononuclear cells | 60-80% neutrophils | > 90% neutrophils | 50 – 70% neutrophils |
* ได้แก่ crystal induced arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis และ inflammatory arthritis อื่นๆ
TREATMENTS
Empirical Antimicrobial Treatment
ให้ยาต้านจุลชีพทันท่วงทีและเหมาะสม ร่วมกับ Synovial fluid drainage และ adequate debridement (หากมีข้อบ่งชี้) ทั้งนี้ การเลือกชนิดของยาปฏิชีวนะ ขึ้นกับผลตรวจ synovial fluid เบื้องต้น และปัจจัยเสี่ยง
- Gram stain ไม่พบ organism แนะนำ ceftriaxone หรือ cefotaxime
- Gram stain พบ gram positive cocci แนะนำ cloxacillin ขนาดสูง
- Gram stain พบ gram negative cocci หรือ bacilli แนะนำ ceftriaxone หรือ cefotaxime
- ในกลุ่ม IVDU ถ้า gram stain ไม่พบ organism แนะนำ cloxacillin ขนาดสูงร่วมกับ ceftazidime
Definitive Antimicrobial Treatment
ระยะเวลาที่ให้ทั่วไปให้ยาต้านจุลชีพฉีดอย่างน้อย 1-2 สัปดาห์ แล้วต่อด้วยให้ยากินจนครบ 3-4 สัปดาห์
| เชื้อก่อโรค | ยาปฏิชีวนะ |
| Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) | • Cloxacillin 2 g IV q 4h หรือ • Cefazolin 2 g IV q 8h |
| Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) or penicillin allergy |
• Vancomycin 15 mg/kg IV q 12h |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin sensitive) |
• Penicillin G 12-18 MU IV/per day หรือ • Ampicillin 2 g IV q 4h |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin resistant) |
• if susceptible to cephalosporins
• Vancomycin 15 mg/kg IV q 12h |
| Enteric gram-negative bacilli | • Ceftriaxone 2 g IV q 24 hours หรือ • Cefotaxime 2 g IV q 8h หรือ • Ciprofloxacin 400 mg IV q 8-12 hours หรือ 750 mg PO q 12h • Levofloxacin 750 mg IV หรือ 750 mg PO once daily |
| Gram negative bacilli
(e.g. Pseudomonas aeruginosa) |
• Ceftazidime 2 g IV q 8h • Cefepime 2 g IV q 8h |
| Polymicrobial: adjust as susceptibilities require | • Ampicillin/sulbactam 1.5-3 g IV q 4h • Clindamycin 600 mg IV q 6-8 hours + • Ciprofloxacin 400 mg IV or 750 mg PO q 12h หรือ Levofloxacin 750 mg IV or PO once daily |
| Gonococcal arthritis/ Disseminated gonococcal infection |
• Preferred: Ceftriaxone 1 g IV or IM q 24h + Azithromycin 1 g PO × 1 dose • Alternative: (plus Azithromycin) Cefotaxime 1 g IV q 8h
|
OTHER RESOURCES
References
1. อนุภพ จิตต์เมือง. Bone and Joint Infections. Handbook of Infectious Disease [Book Editors: รุจิภาส สิริจตุภัทร, ภาคภูมิ พุ่มพวง, วลัยพร วังจินดา]. 2nd. กรุงเทพมหานคร : สาขาวิชาโรคติดเชื้อและอายุรศาสตร์เขตร้อน ภาควิชาอายุรศาสตร์ คณะแพทยศาสตร์ ศิริราชพยาบาล มหาวิทยาลัยมหิดล, 2021, pp. 196-201.
2. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s. Infectious Arthritis of Native Joint. Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. ninth. s.l. : Elsevier, Inc., 2020, p. 103.
3. Valeria Fabre, M.D., Paul G. Auwaerter, M.D. Septic Arthritis (Native). Johns Hopkins ABX Guide. s.l. : Johns Hopkins University, 2020.
